
Hence, these proteins represent important therapeutic targets for drug discovery. Not only dysregulation or dysfunction of P-type ATPases, but also mutations in their genes are often associated with human diseases.

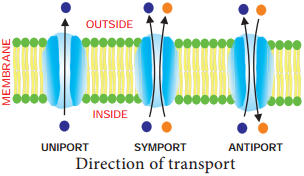
The members of the P-type ATPases share a general characteristic architecture and working mechanism but, at the same time, are unique proteins through their specificity to the substrate, mode of regulation, subcellular localization and tissue distribution. Therefore, they allow interaction between the extracellular and intracellular environment and serve as critical mediators of physiological activities of cells and organelles. diffusion, osmosis (or water diffusion) and facilitated diffusion ( or diffusion with a protien channel. there are three kinds of passive transport. They play a key role in a broad range of cellular functions such as generating vitally important ion gradients, uptake or extrusion of heavy metals or polyamines, controlling lipid asymmetry and vesicle formation in membranes. passive transport moves small molecules without the use of energy. Semi-permeable membranes are very thin layers of material that allow some things to pass through them but prevent other things from passing through.P-type ATPases operate as molecular pumps in cells and transport various substrates across biological membranes using ATP as the energy source. Water moves in or out of a cell until its concentration is the same on both sides of the plasma membrane.
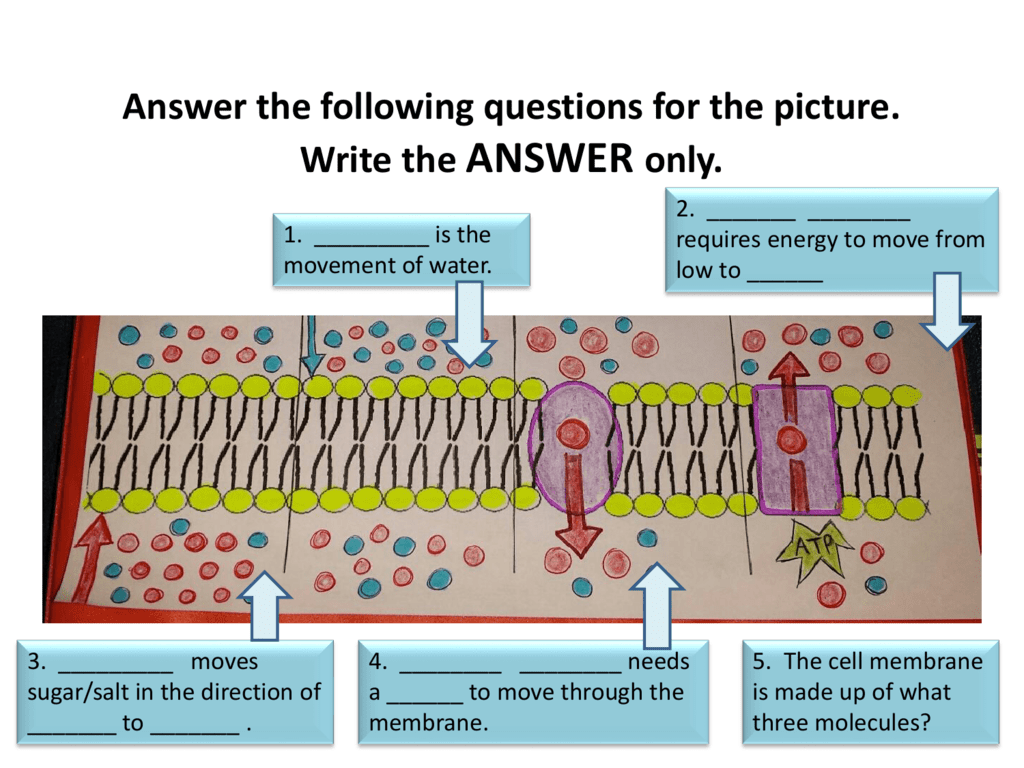
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion it is the passage of water from a region of high water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane to a region of low water concentration. In living systems, diffusion is responsible for the movement of a large number of substances, such as gases and small uncharged molecules, into and out of cells. Both living and nonliving systems experience the process of diffusion. The equilibrium is said to be dynamic because molecules continue to move, but despite this change, there is no net change in concentration over time. Once the molecules become uniformly distributed, a dynamic equilibrium exists. This unequal distribution of molecules is called a concentration gradient.
This spread of particles through the random motion from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration is known as diffusion. Odors diffuse through the air, salt diffuses through water and nutrients diffuse from the blood to the body tissues. Thus, the net movement of molecules is always from more tightly packed areas to less tightly packed areas. Over time, however, more molecules will be propelled into the less concentrated area. These collisions cause the molecules to move in random directions. Molecules are in constant movement and collide with each other.
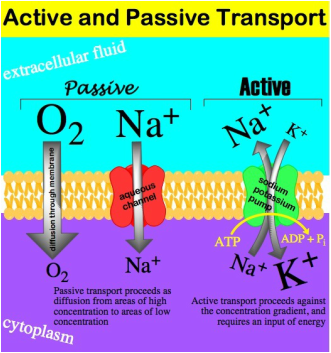
A cell must expend energy to transport substances using. The molecules in a gas, a liquid, or a solid are in constant motion due to their kinetic energy. The SHRINKING of plant cells when water leaves so the cell membrane. Over time, they diffuse into the cell until there is an equal amount outside and inside. In the beginning of the timeline there are many molecules outside of the cell and none inside. Simple diffusion shows as a timeline with the outside of the cell (extracellular space) separated from the inside of the cell (intracellular space) by the cell membrane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
